Dr CHAN Kin Ming Kevin and Dr. LEE Shui Kwong John, the two specialists in Otorhinolaryngology (ENT) from Chiron Medical point out that the sensation of a foreign body in the throat is a common issue many people face in their daily lives. It refers to the feeling of something being stuck in the throat, despite the absence of any actual obstruction. Patients often describe it as feeling like a lump of phlegm, food particles, or even a small ball lodged in the throat, making it difficult to swallow or expel. Some may even experience a tightening sensation, akin to being choked. This feeling is medically termed globus pharyngeus. It is not a disease but a symptom that can lead to anxiety and distress due to its persistent nature, necessitating further exploration of its causes and seeking treatment.
Common Causes of a Foreign-body Sensation in Throat
There are numerous factors that can contribute to the sensation of a foreign body in the throat, ranging from simple muscle tension to chronic conditions. Here are some common triggers:
- Muscle Tension (Globus Pharyngeus): Stress or anxiety can cause the throat muscles to contract, giving the feeling of obstruction, although swallowing food is usually unaffected.
- Chronic Pharyngitis: Repeated inflammation, postnasal drip, or gastroesophageal reflux can irritate the throat, leading to a persistent sense of blockage.
- Postnasal Drip: Excess mucus from allergies or sinusitis can flow back into the throat, causing discomfort.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Acid reflux can lead to inflammation and burning in the throat, which may create a sensation of a foreign body.
- Tonsil Stones: Accumulation of food debris and bacteria can form small white stones, leading to a feeling of blockage and bad breath.
- Thyroid Enlargement or Nodules: Pressure on the trachea or esophagus can create a persistent sensation of obstruction.
- Psychological Factors: Anxiety and tension can trigger autonomic nervous responses, causing the throat muscles to tighten.
These factors may overlap, and patients need a doctor's examination to identify the true cause.
Warning Signs to Watch For
While most sensations of a foreign body in the throat are benign, certain "danger signals" necessitate caution, as they may indicate underlying serious conditions. Warning signs include:
- Persistent Throat Pain or Hoarseness: These may be early signs of chronic inflammation or tumors.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Pain While Swallowing: Especially if accompanied by choking or coughing during meals.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: If accompanied by decreased appetite, serious conditions should be ruled out.
- Coughing Up Blood: This could be related to ulcers or tumors.
- Neck Mass or Difficulty Breathing: Requires examination of thyroid or lymph node abnormalities.
If the sensation persists for more than two weeks without improvement, or if any of the above symptoms occur, it is advisable to seek medical attention promptly to avoid delaying diagnosis.
Common Diagnostic Methods Used by Doctors
Based on symptoms and medical history, doctors will arrange a series of examinations to determine the cause. Common tests include:
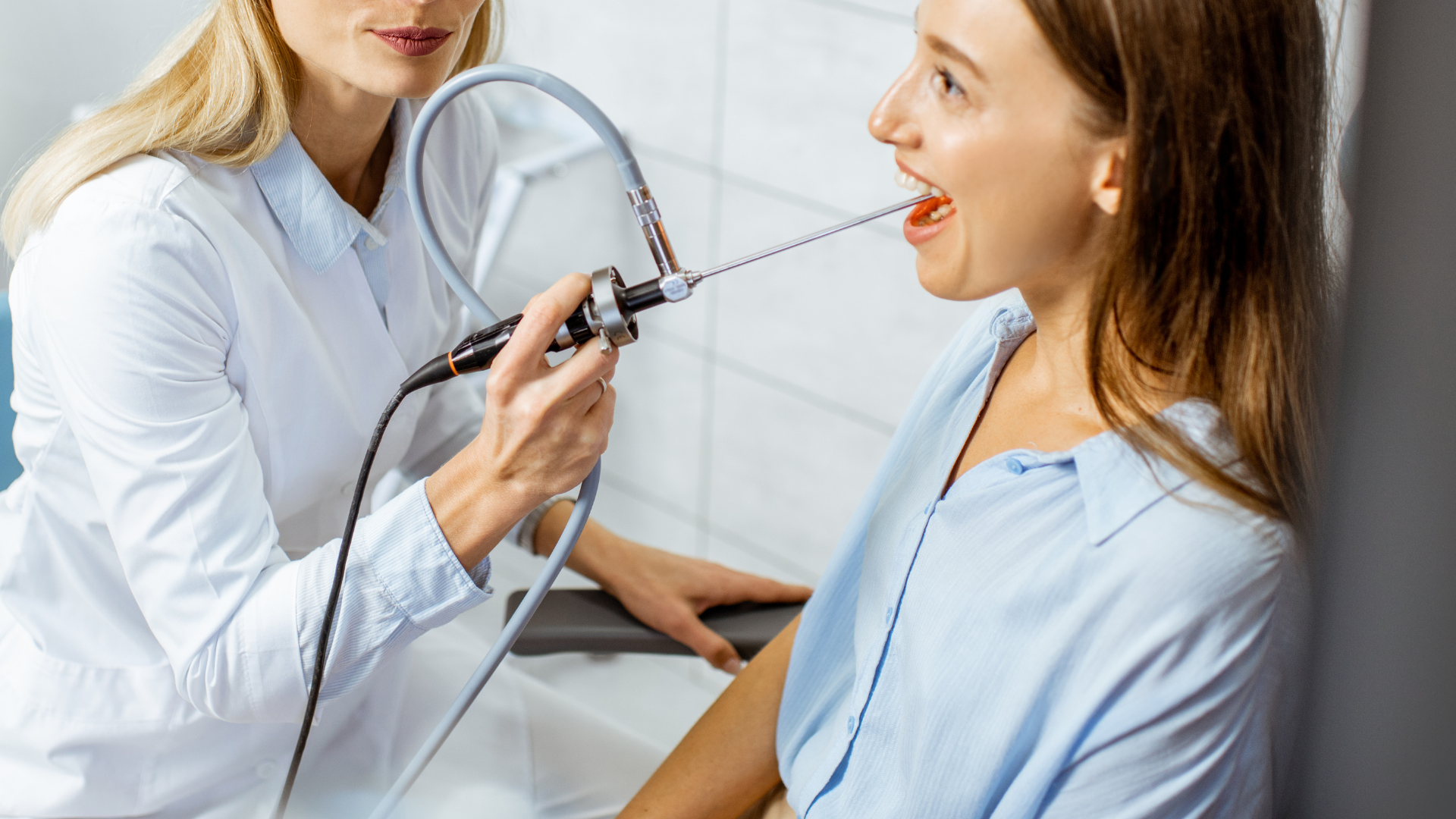
- ENT Endoscopy: Observing the throat, vocal cords, and esophageal entrance for inflammation or tumors.
- Neck Ultrasound: Checking the size of the thyroid, nodules, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Upper Endoscopy and Barium Swallow Tests: Evaluating for acid reflux or esophageal narrowing.
- Imaging Tests (X-ray, CT, MRI): Assessing deeper tissues, bones, or tumors.
- Biopsy: If suspicious masses are found, tissue samples may be taken to determine malignancy.
These tests effectively help rule out serious conditions and clarify the causes of the sensation of a foreign body in the throat.

Treatment and Relief Methods for a Foreign-body Sensation in Throat
Treatment must target the underlying cause and be complemented by lifestyle adjustments. Common management strategies include:
- Treating Inflammation or Postnasal Drip: Controlling rhinitis or tonsillitis with local medications to alleviate discomfort.
- Improving Gastroesophageal Reflux: Using antacids and adjusting eating habits (frequent small meals, avoiding irritants) to prevent further throat irritation.
- Psychological Adjustments: If caused by emotional factors, anti-anxiety medications or muscle relaxants may be prescribed under medical guidance.
Daily habits should also be adjusted to promote relaxation and overall well-being, including neck stretches and deep breathing exercises to relieve throat tension.

Self-Management in Daily Life
In addition to treatment, adjusting daily habits is crucial for alleviating symptoms. It's recommended to:
- Chew Slowly: Ensure each bite is chewed 15-20 times to avoid hurried swallowing.
- Eat Smaller Meals More Frequently: Avoid overeating and refrain from eating at least three hours before bedtime.
- Avoid Irritants: Quit smoking and drinking, limit fried and spicy foods, and reduce caffeine intake.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water and use a humidifier to keep the throat moist, avoiding excessive throat clearing.
- Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule: Ensure adequate sleep and manage stress levels effectively.
These seemingly simple habits can significantly improve the sensation of a foreign body in the throat, especially when combined with the treatments recommended by your doctor. Our ENT specialty centre has an experienced medical team ready to provide professional examinations and treatment services. Schedule your appointment today! Click here to book a consultation with a specialist.

Updated: 2025-09
Please note that all medical health articles featured on our website have been reviewed by Chiron Medical doctors. The articles are for general information only and are not medical opinions nor should the contents be used to replace the need for personal consultation with a qualified health professional on the reader's medical condition.



